Purchase to pay
What? Purchase to Pay refers to a series of operations in an organization, from purchase to payment.
Why? Improving Purchase to Pay is expected to improve operational efficiency across the business.
How? Purchase to Pay process mining can be analyzed from four main improvement perspectives (cycle time, cost, operational efficiency and digitalization).
Purchase to Pay is a set of processes from procurement to payment.
Purchase to Pay (also known as P2P, Procure to Pay) is a series of operations from procurement to payment that are necessary when companies procure direct/indirect materials. It refers to a series of operations from supplier selection to supplier payment.
The P2P process consists of five main stages.
- purchase requisition
- purchase order
- goods receipt
- invoice
- payment.
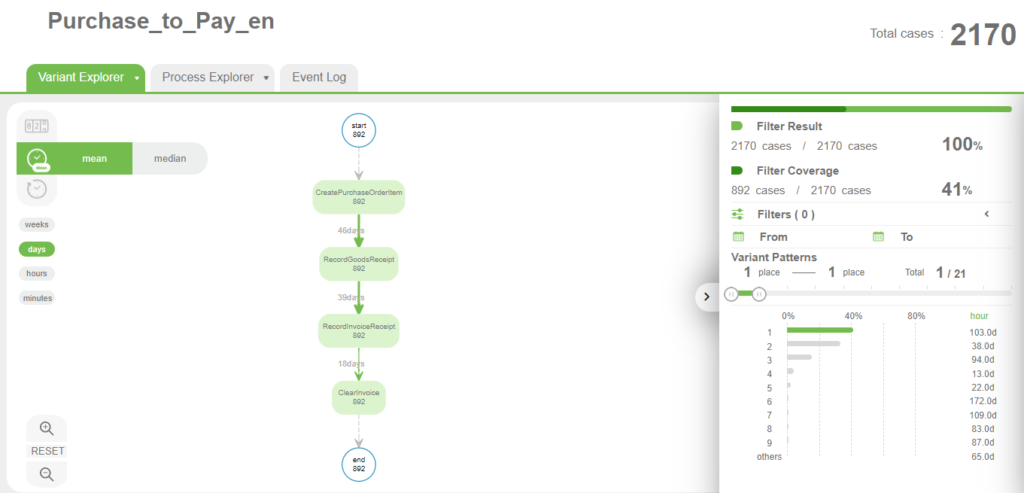
In process mining, event data around these five phases is represented as a process diagram.
SAP explains Purchase to Pay. To learn more, click here ↓.
https://www.sap.com/products/spend-management/procure-to-pay/what-is-procure-to-pay.html
Analysis of P2P processes provides clues for improving operational efficiency
So why improve your P2P processes? The reason is the potential to improve company-wide operational efficiency (time and cost savings). The world is moving faster and services need to be delivered in less time to stay ahead of the competition. This shorter delivery time can be achieved by reducing throughput time through improved P2P processes. It may also be possible to protect your own profits and therefore gain an advantage over your competitors by reducing costs.
Within the P2P process, it is important to focus on supplier efficiency. This is because goods purchased from suppliers represent a high proportion of total costs.
Therefore, P2P processes need to be improved in order to gain an advantage over competitors, and it is important to focus on and analyze supplier relationships, among other things.
Use cases for P2P Process Mining
The use cases for P2P Process Mining can be broadly divided into the following four improvement perspectives
- Lead time reduction Process Explorer analysis uncovers the potential for reducing lead times of activities and identifies the root causes of inefficiencies, e.g. suppliers, purchasing organizations, transporters, etc.
- improve operational efficiency Eliminating inefficient processes and fraudulent practices can reduce operational inefficiencies.
- optimize working capital Compare different payment terms on master data, POS and invoices with Process Explorer to discover more favorable payment terms.
- digitize your operations Implement EDI* by connecting external suppliers with message types such as purchase orders, order processing, order changes, invoices, delivery forecasts and stock reports.
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange, or EDI): the automatic exchange of electronic records and documents between businesses and government agencies by linking computers through networks.
The following section describes specific examples for each improvement perspective.
1. Discovering the opportunity to reduce cycle time by identifying rework
If the problem is that the lead time from ‘order creation’ to ‘goods receipt’ is long, root cause analysis is effective. By observing the Process Explorer when the cycle time is long, we discovered the occurrence of a rework activity called ‘quantity change’. This indicates that the cycle time is longer because the quantity change requires more goods to be delivered than originally planned. The fact that the lead time is longer in cases where a ‘quantity change’ has occurred than in cases where it has not indicates that the occurrence of ‘quantity changes’ should be minimized.
2. Fraud detection.
Observing P2P processes in the Process Explorer can also help to detect fraud. Cases where ‘Order Creation’ occurs after ‘Invoicing’ are suspicious of fraudulent activity. Thus, by discovering the order in which suspicious activities occur, the occurrence of fraud can be identified. By correcting fraud as it is identified, risks can be reduced and operational efficiency can be improved by improving the process for dealing with discrepancies.
3. Availability of discounts for meeting payment terms.
Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payment. For example, cost savings can be achieved by negotiating terms of (i) a 3% discount for payment within 14 days and (ii) no discount for payment over 60 days. By looking at the Process Explorer for each supplier and identifying which suppliers can and cannot deliver within 14 days, you can select suppliers to negotiate terms with.
4. Go digital by encouraging the use of EDI
Using email and fax to communicate with suppliers about orders and payments is manual and prone to errors that require significant effort and rework. In addition, responding to errors and change requests can lead to payment delays and additional rework due to data discrepancies.
To improve this inefficiency, it is effective to manage all communication electronically. Message types such as purchase orders, order processing, changes, concept notes and invoices can be packaged via EDI to improve speed, quality and efficiency.
Process mining can reveal that EDI suppliers achieve better operational efficiency by comparing non-EDI suppliers’ processes with those of EDI suppliers; the increase in EDI-enabled sites reduces rework, resulting in a significant reduction in lead time.
These are specific use cases for P2P Process Mining. There are four main improvement perspectives: throughput time reduction by finding rework, fraud detection by finding unnatural process sequences, optimization of working capital by negotiating payment terms, and digitization by using EDI.
Conclusion (improving orders can do a lot of good!)
The P2P process refers to the sequence of operations from procurement to payment. This process needs to be improved in order to gain an edge over the competition – improving P2P processes can lead to various benefits for the company, such as reduced lead times, increased operational efficiency and optimized costs, which in turn helps to protect the company’s overall profitability. Process Mining is a technology that provides you with pinpoints on the processes and indicators you want to look at when analyzing these improvement perspectives – discover the improvement potential of your P2P processes and aim to improve your operational efficiency!



